Although the Korean shipbuilding industry is experiencing a resurgence often referred to as its “second golden age,” it continues to face challenges in securing skilled labor. While the gap is partially filled with foreign workers, tasks like welding require extensive training due to the need for expertise and craftsmanship. Furthermore, once workers become proficient, many leave due to visa or residency limitations.
To address this, HD Hyundai Samho has adopted collaborative robots for welding automation. Welding is a critical process in shipbuilding, directly impacting structural integrity and overall vessel quality. HD Hyundai Samho, a global shipbuilding and marine company constructing over 50 ships annually, chose robotic welding automation as a way to reduce labor intensity and increase production efficiency.
JCT, a partner specializing in welding systems, joined this project. As a robotics automation company with strong expertise in component technologies and system integration, JCT delivers customized solutions using Rainbow Robotics’ RB series collaborative robots across factory automation, logistics, and service robotics. Beyond robotic systems, JCT also integrates various automation components such as PLCs, HMIs, and sensors to provide comprehensive SI solutions. With experience in both industrial and collaborative robots, JCT identified the RB series as the optimal choice for this process and supplied the solution to HD Hyundai Samho. Unlike industrial robots that require safety fences, collaborative robots can work alongside human operators without additional enclosures, offering greater efficiency in space and cost.
Welding ensures the strength and stability of ship structures. Previously, welding was done manually or using carriage systems. However, securing additional manpower became difficult, and carriage systems could not achieve full automation. These systems follow straight paths but struggle in closed or confined spaces due to limitations in welding start and end points.
Recognizing the need for flexibility and precision in constrained environments, HD Hyundai Samho adopted Rainbow Robotics’ RB3-730 collaborative robot. This decision enabled high-quality welding even in tight shipyard blocks, overcoming the limitations of carriage welding. Furthermore, the company is actively researching the use of collaborative robots in curved block welding applications to maximize their advantages.
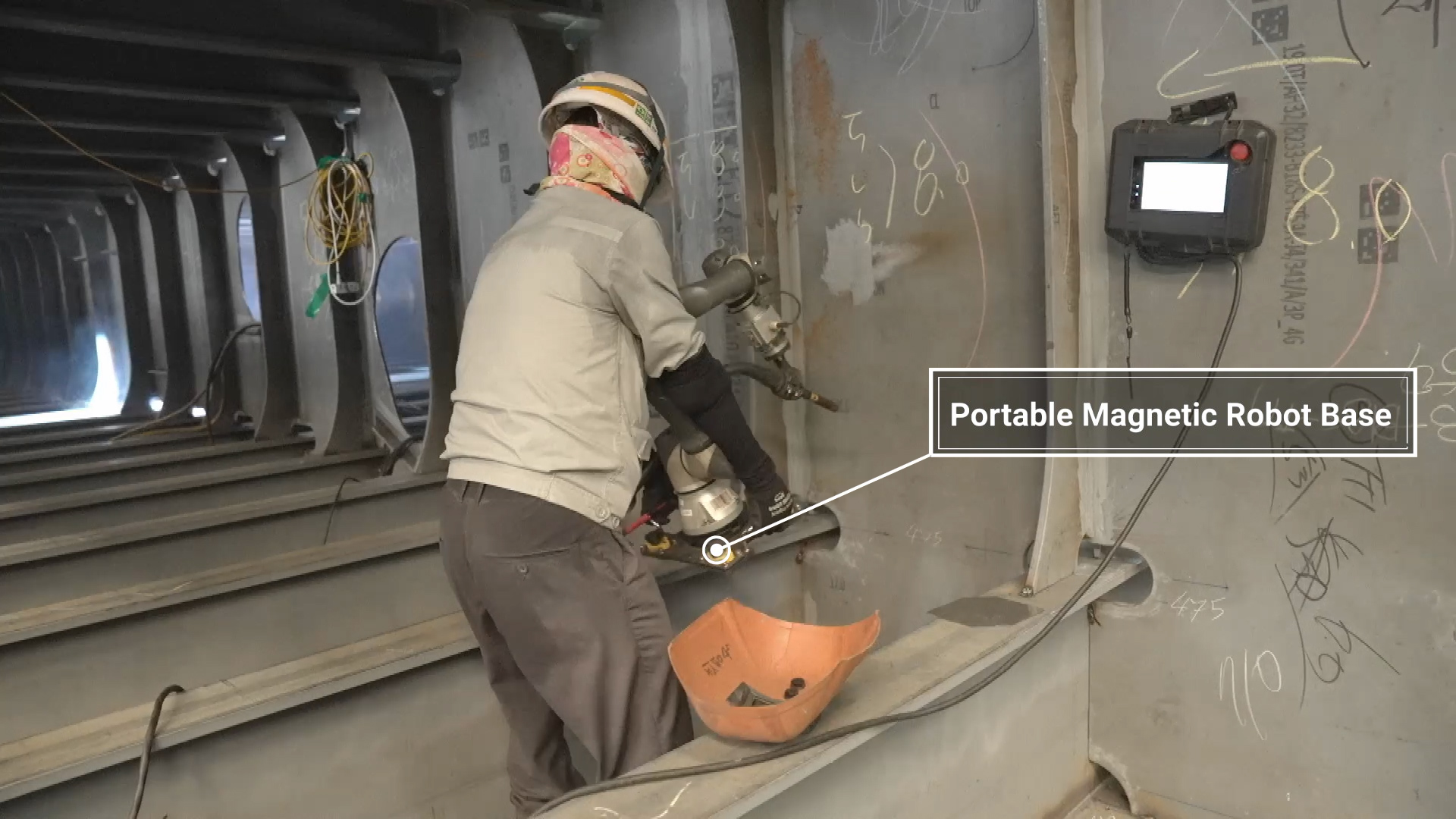
A Portable Welding System with Mobility and Precision
The RB3-730, a compact high-precision collaborative robot, features an S-shaped arm configuration ideal for complex contours. Its three wrist joints rotate through a common point, allowing for precise and efficient movements. These structural benefits make the RB3-730 widely suitable for welding automation.
With a payload capacity of 3kg and a weight of 11kg, it is well-suited for mounting welding torches. Using these features, a portable welding system was developed that workers can carry directly. The magnetic robot base provides stable support during welding, while handles on both sides of the 14kg total system (including the robot) allow easy transport and ergonomic handling.

Precision Welding Enabled by Built-In RB Software
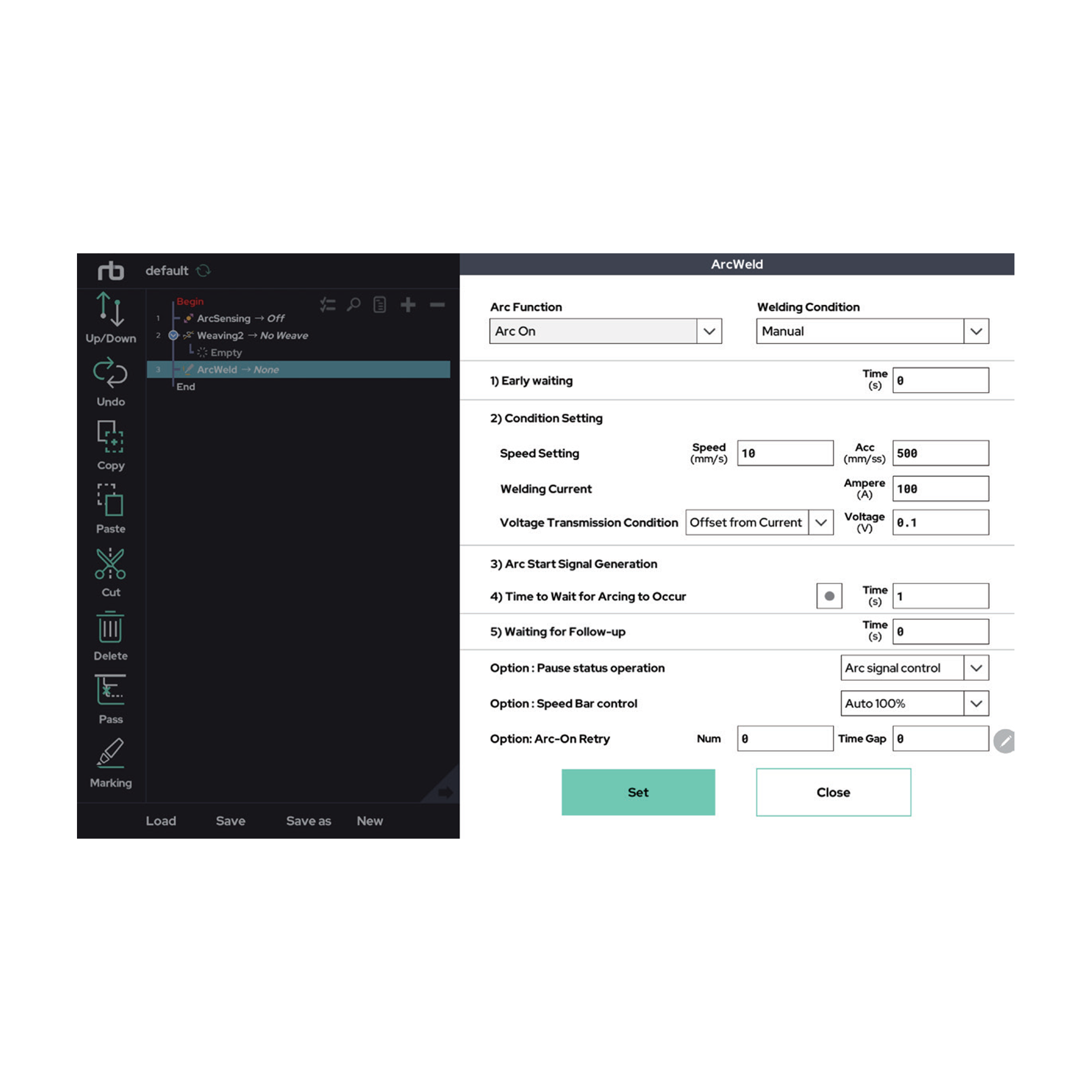
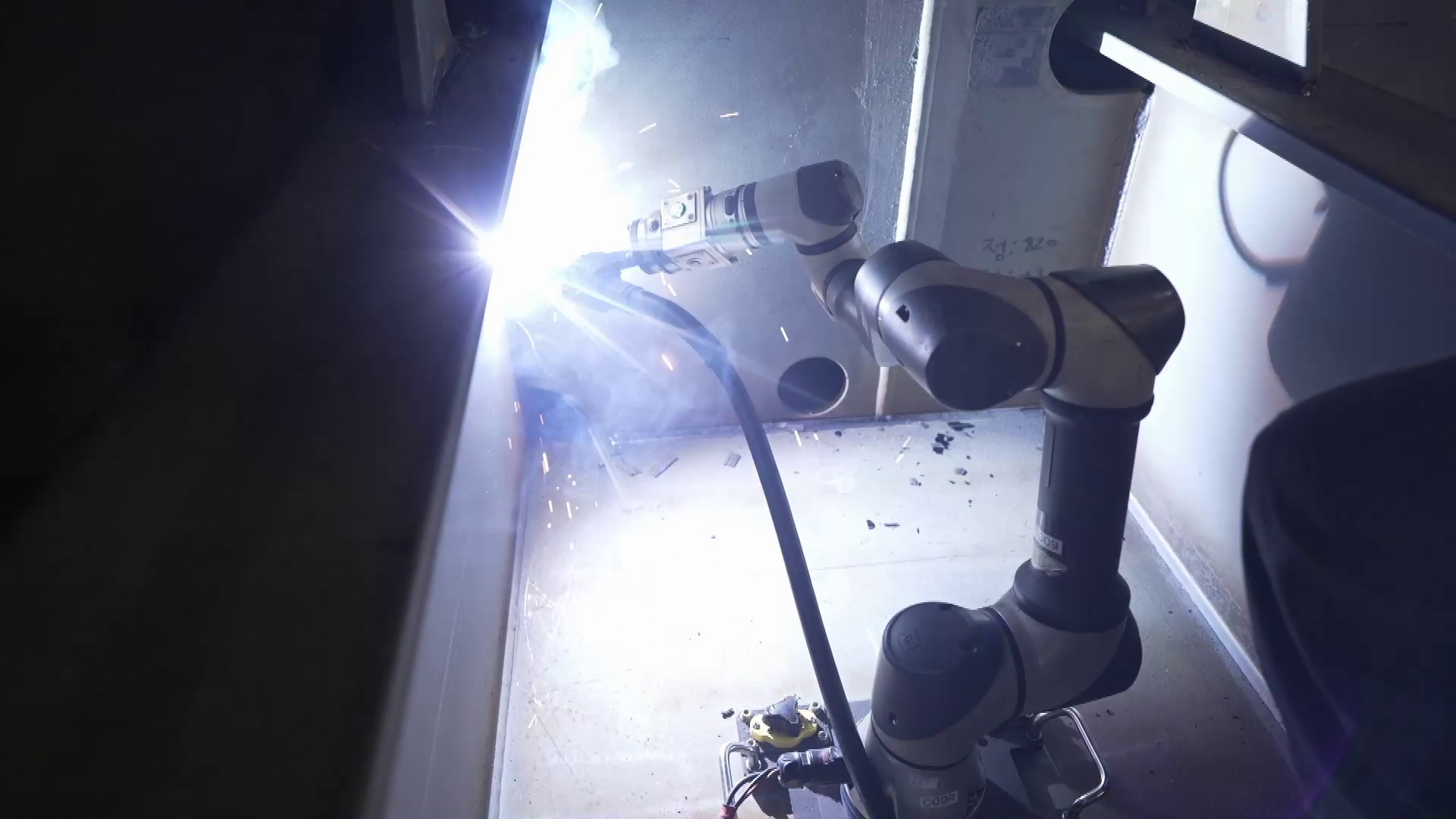
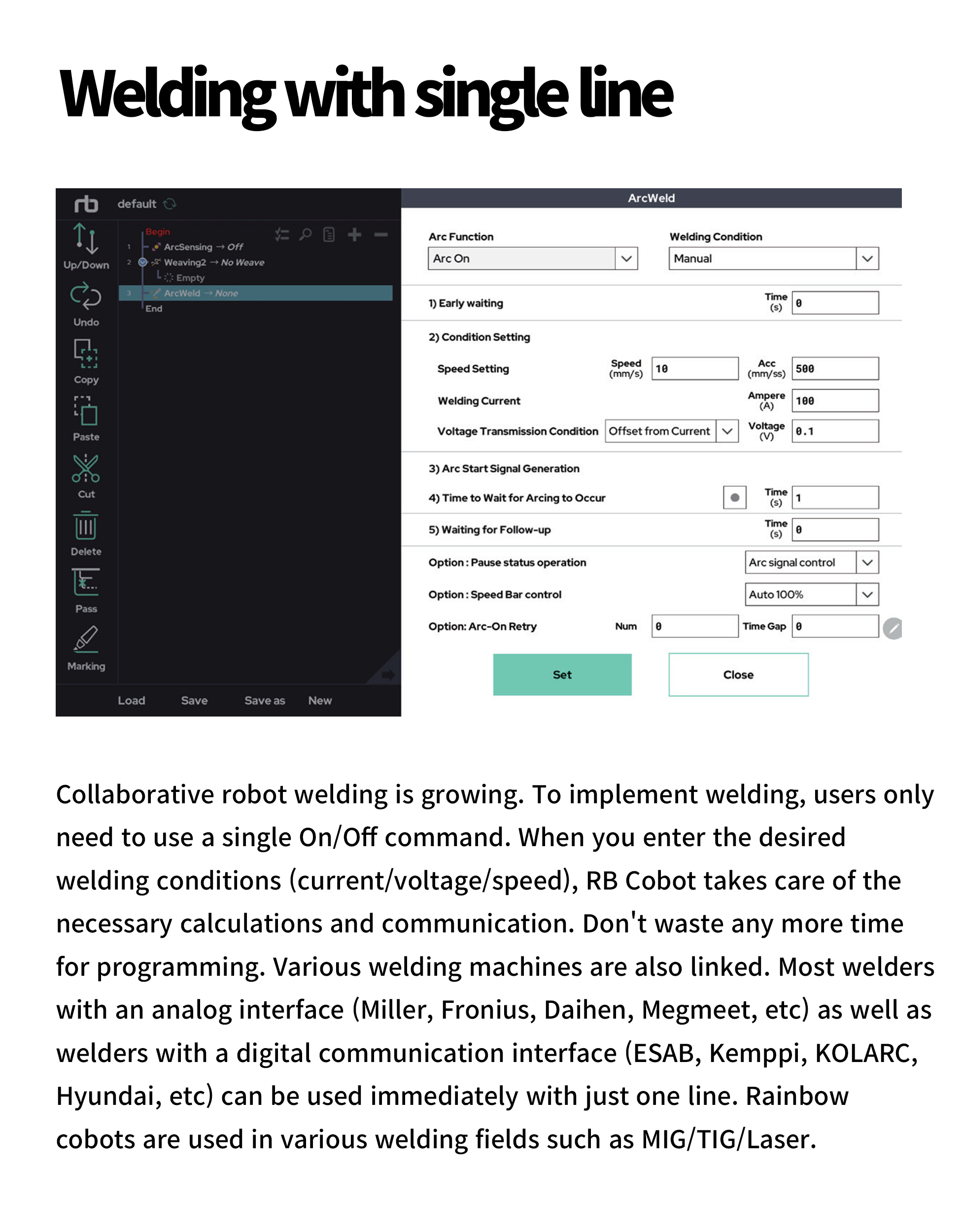
The RB series offers the most built-in functionalities among collaborative robots in its class. These features are standard capabilities provided by the manufacturer, enabling use across various processes without the need for additional programming or costs. In particular, advanced welding automation software such as seam tracking via arc sensing, touch sensing, and TIG gap maintenance functions are pre-installed, making the system adaptable to a wide range of working conditions. Additionally, the integration of auxiliary axes and synchronized control maximizes the potential applications of robotic welding.
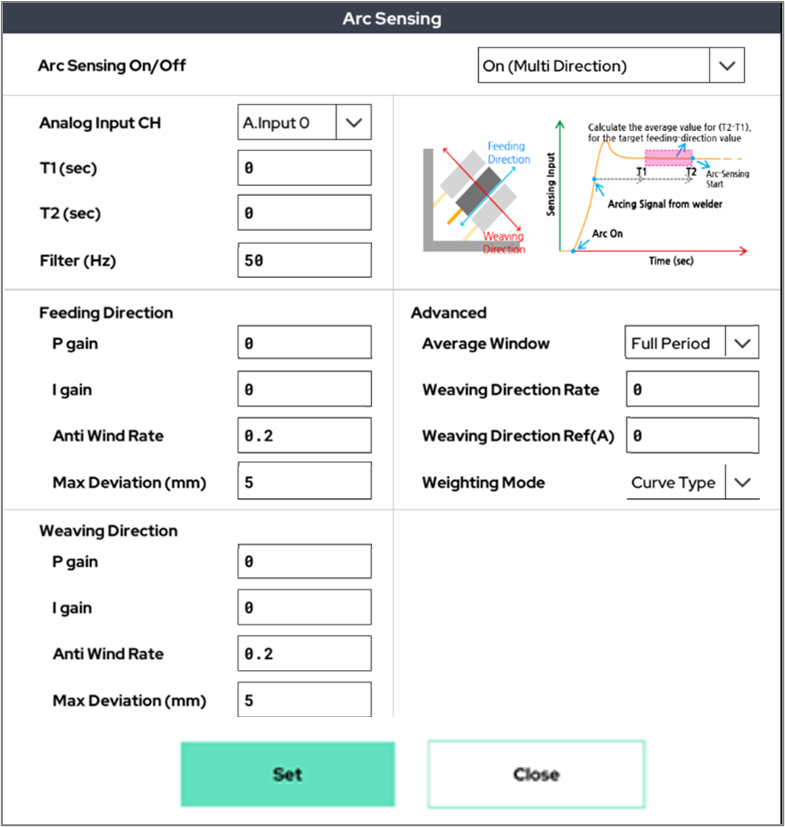
This process utilizes arc welding, a method that joins metals by generating an electric arc between the electrode and the base material. Three main welding functions are primarily used: arc sensing, touch sensing, and weaving motion.Arc Sensing (Arc Tracking): Tracks the weld seam centerline and adjusts height between workpiece and torch in real time using welding current data. Both unidirectional and bidirectional arc sensing are supported, the latter being required for weaving operations. Applicable to MIG/TIG welding.

● Arc Sensing Function for Weld Seam Tracking
Rainbow Robotics’ collaborative robots come equipped with seam-tracking capabilities through arc sensing. This feature enables the robot to automatically follow the weld seam while adjusting the height between the base material and the electrode in real time during the welding process. It also compensates for deviations caused by material distortion or inaccuracies in teaching, maintaining consistent weld quality by utilizing current feedback from the welding machine. Arc sensing is categorized into unidirectional and multidirectional modes, with the latter required when used in combination with weaving. This functionality supports a variety of welding methods, including MIG and TIG.
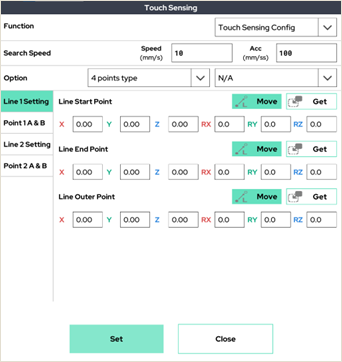
● Touch Sensing Function for Detecting Base Material
The touch sensing function is designed to enhance welding applications. It detects the movement of the base material and reflects its direction in the welding process. This allows the robot to fine-tune the position of the electrode relative to the joint or surface of the material, ensuring precise alignment for optimal weld quality.
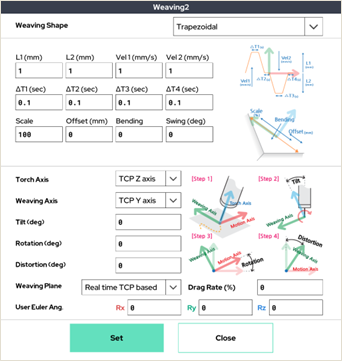
● Various Weaving Profiles
Weaving motion plays a crucial role in welding processes. Rainbow Robotics’ collaborative robots feature a user interface that includes built-in capabilities for creating various weaving patterns and profiles. The system supports a wide range of shapes commonly required in welding sites, such as trapezoidal, triangular, sine wave, square wave, sawtooth, and circular patterns. Users can simply select a shape and parameters to implement weaving motions easily, eliminating the need for time-consuming manual programming.

"Rainbow Robotics’ collaborative robots seamlessly integrate with various MIG and TIG welding machines without coding, and their built-in user interface functions automatically control safety features based on robot status. In industrial settings like HD Hyundai Samho, these capabilities are combined to deliver high-quality welding results."
Ph D. Hyo-In Bae is Principal Researcher in the SW1 Team at Rainbow Robotics, where he leads the development of software for collaborative robots.Improved On-Site Efficiency Post-Deployment
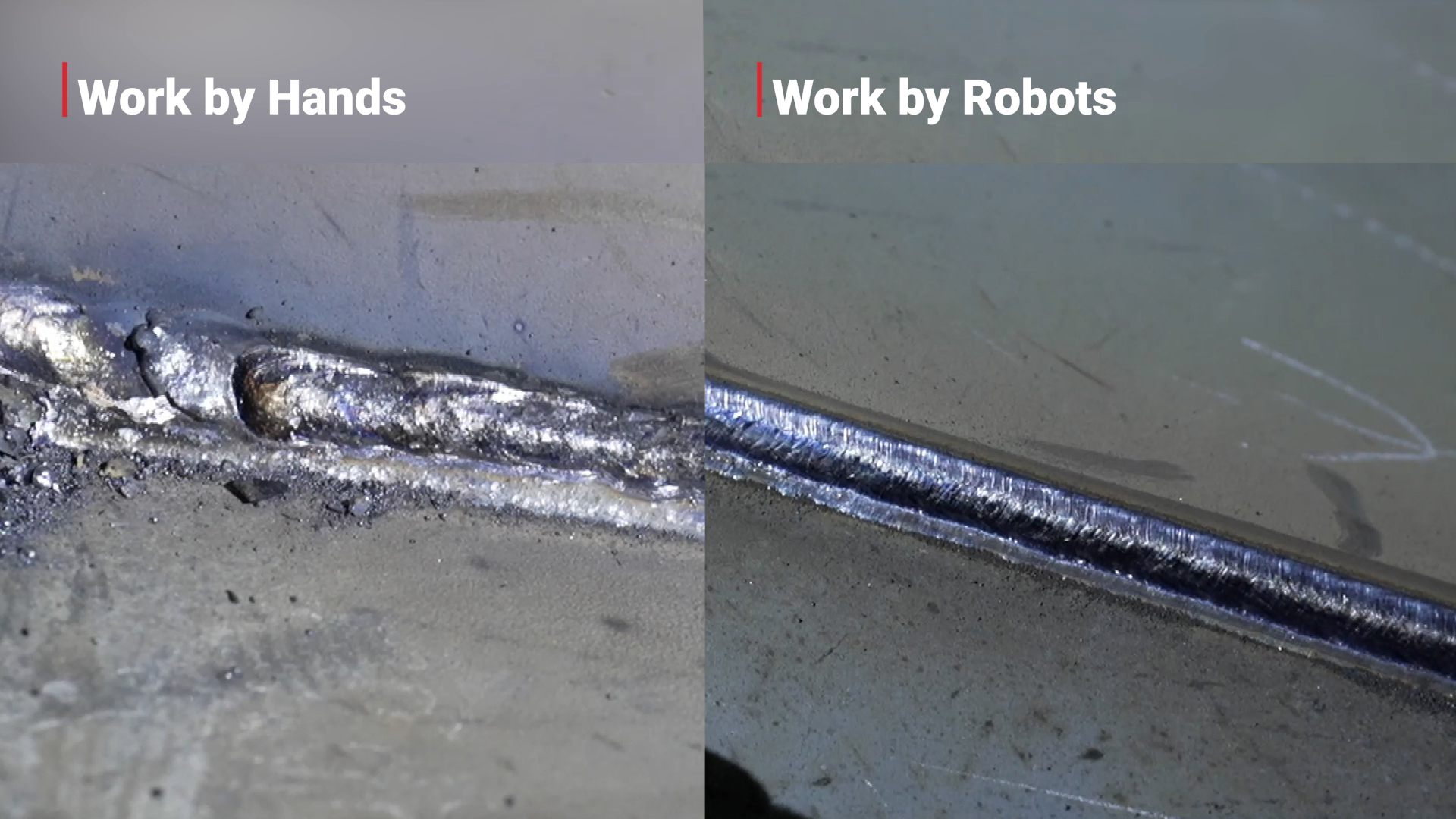
Since adopting the system, HD Hyundai Samho has seen improvements in work speed and overall productivity, along with more consistent weld quality. While manual welding takes about 13 minutes per flat block and the robot takes around 15 minutes, robots can work continuously without breaks.
In a day, a robot can weld up to 50 steel plates, compared to 25 by a human welder — doubling daily output. Manual welding can lead to quality variations and potential rework, while robots provide high precision from the start, eliminating such inconsistencies.
Additionally, a collaborative robot monitoring system collects real-time data on work hours, peak times, welding quantity, and robot operation rates. This enables data-driven forecasting and deployment, leading to more efficient manpower and equipment management based on workload.
Setting a New Standard for Automation in Shipbuilding
This project proves the real-world applicability of portable collaborative robot systems in the demanding environments of the shipbuilding industry. It demonstrates how collaborative robots can provide the necessary flexibility and precision in even the most complex manufacturing processes. Rainbow Robotics remains committed to leading automation innovations across various industrial sectors.

Related products
Case Study
사이트 개인정보 보호 정책
㈜ 레인보우로보틱스(이하 “회사”라 함)는 「개인정보 보호법」 제30조에 따라 정보주체의 개인정보를 보호하고 이와 관련한 고충을 신속하고 원활하게 처리할 수 있도록 하기 위하여 다음과 같이 개인정보 처리방침을 수립·공개합니다.
제1조(개인정보의 처리목적)회사는 다음의 목적을 위하여 개인정보를 처리합니다. 처리하고 있는 개인정보는 다음의 목적 이외의 용도로는 이용되지 않으며 이용 목적이 변경되는 경우에는 「개인정보 보호법」 제18조에 따라 별도의 동의를 받는 등 필요한 조치를 이행할 예정입니다.
-
1.홈페이지 회원가입 및 관리
회원 가입의사 확인, 회원제 서비스 제공에 따른 본인 식별·인증, 회원자격 유지·관리, 서비스 부정이용 방지, 각종 고지·통지 목적으로 개인정보를 처리합니다. -
2.민원사무 처리
민원인의 신원 확인, 민원사항 확인, 사실조사를 위한 연락·통지, 처리결과 통보 목적으로 개인정보를 처리합니다. -
3.서비스 제공
콘텐츠 제공, 본인인증을 목적으로 개인정보를 처리합니다. -
4.마케팅 및 광고에의 활용
신규 서비스(제품) 개발 및 맞춤 서비스 제공, 이벤트 및 광고성 정보 제공 및 참여기회 제공, 서비스의 유효성 확인, 접속빈도 파악 또는 회원의 서비스 이용에 대한 통계 등을 목적으로 개인정보를 처리합니다.
- ①회사는 법령에 따른 개인정보 보유·이용기간 또는 정보주체로부터 개인정보를 수집 시에 동의받은 개인정보 보유·이용기간 내에서 개인정보를 처리·보유합니다.
- ②각각의 개인정보 처리 및 보유 기간은 다음과 같습니다.
| 보존항목 | 운영근거 | 보유기간 |
|---|---|---|
| 홈페이지 회원가입 및 관리와 관련한 개인정보 | 정보주체 동의 | 3년 |
| 개인정보 열람 등 요구 처리 사용자 정보 | 개인정보보호법 제35조-제39조 | 3년 |
| 문의와 관련한 개인정보 | 정보주체 동의 | 1년 |
| 서비스 방문 기록 | 통신비밀보호법 | 1년 |
- ①정보주체는 회사에 대해 언제든지 개인정보 열람·정정·삭제·처리정지 요구 등의 권리를 행사할 수 있습니다.
- ②제1항에 따른 권리 행사는 회사에 대해 「개인정보 보호법」 시행령 제41조제1항에 따라 서면, 전자우편, 모사전송(FAX) 등을 통하여 하실 수 있으며 회사는 이에 대해 지체 없이 조치하겠습니다.
- ③제1항에 따른 권리 행사는 정보주체의 법정대리인이나 위임을 받은 자 등 대리인을 통하여 하실 수 있습니다. 이 경우 “개인정보 처리 방법에 관한 고시(제2020-7호)” 별지 제11호 서식에 따른 위임장을 제출하셔야 합니다.
- ④개인정보 열람 및 처리정지 요구는 「개인정보 보호법」 제35조 제4항, 제37조 제2항에 의하여 정보주체의 권리가 제한될 수 있습니다.
- ⑤개인정보의 정정 및 삭제 요구는 다른 법령에서 그 개인정보가 수집 대상으로 명시되어 있는 경우에는 그 삭제를 요구할 수 없습니다.
- ⑥회사는 정보주체 권리에 따른 열람의 요구, 정정·삭제의 요구, 처리정지의 요구 시 열람 등 요구를 한 자가 본인이거나 정당한 대리인인지를 확인합니다.
-
1.채용/구매/제품/기타문의
이름, 이메일 등 기재정보 -
2.인터넷 서비스 이용과정에서 아래 개인정보 항목이 자동으로 생성되어 수집될 수 있습니다.
IP주소, 쿠키, MAC주소, 서비스 이용기록, 방문기록, 불량이용기록 등
- ①회사는 개인정보 보유기간의 경과, 처리목적 달성 등 개인정보가 불필요하게 되었을 때에는 지체없이 해당 개인정보를 파기합니다.
- ②개인정보 파기의 절차 및 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
-
1.파기절차
회사는 파기 사유가 발생한 개인정보를 선정하고, 회사의 개인정보 보호책임자의 승인을 받아 개인정보를 파기합니다. -
2.파기방법
전자적 파일 형태의 정보는 기록을 재생할 수 없는 기술적 방법을 사용합니다.
종이에 출력된 개인정보는 분쇄기로 분쇄하거나 소각을 통하여 파기합니다
회사는 개인정보의 안전성 확보를 위해 다음과 같은 조치를 취하고 있습니다.
- 1.관리적 조치: 개인정보 취급 직원의 최소화 및 교육, 내부관리계획 수립 및 시행 등
- 2.기술적 조치: 해킹 등에 대비한 기술적 대책, 개인정보의 암호화, 개인정보에 대한 접근 제한, 문서보안을 위한 잠금장치 사용 등
- ①회사는 이용자에게 개별적인 맞춤서비스를 제공하기 위해 이용정보를 저장하고 수시로 불러오는 ‘쿠키(cookie)’를 사용합니다.
-
②쿠키는 웹사이트를 운영하는데 이용되는 서버(http)가 이용자의 컴퓨터 브라우저에게 보내는 소량의 정보이며 이용자들의 PC 컴퓨터내의 하드디스크에 저장되기도 합니다.
- 가.쿠키의 사용 목적 : 이용자가 방문한 각 서비스와 웹 사이트들에 대한 방문 및 이용형태, 인기 검색어, 보안접속 여부, 등을 파악하여 이용자에게 최적화된 정보 제공을 위해 사용됩니다.
- 나.쿠키의 설치•운영 및 거부 : 웹브라우저 상단의 도구>인터넷 옵션>개인정보 메뉴의 옵션 설정을 통해 쿠키 저장을 거부 할 수 있습니다.
- 다.쿠키 저장을 거부할 경우 맞춤형 서비스 이용에 어려움이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- ①회사는 개인정보 처리에 관한 업무를 총괄해서 책임지고, 개인정보 처리와 관련한 정보주체의 불만처리 및 피해구제 등을 위하여 아래와 같이 개인정보 보호책임자를 지정하고 있습니다.
성명: 이정호 대표이사
► 개인정보 보호 담당부서
부서명: 마케팅팀
담당자: 김유림
연락처: 전화) 042-719-8104, 팩스) 042-719-8071, 이메일) yr.kim@rainbow-robotics.com
- ①정보주체는 회사의 서비스(또는 사업)을 이용하시면서 발생한 모든 개인정보 보호 관련 문의, 불만처리, 피해구제 등에 관한 사항을 개인정보 보호책임자 및 담당부서로 문의하실 수 있습니다. 레인보우로보틱스 은(는) 정보주체의 문의에 대해 지체 없이 답변 및 처리해드릴 것입니다.
정보주체는 「개인정보 보호법」 제35조에 따른 개인정보의 열람 청구를 아래의 부서에 할 수 있습니다. 회사는 정보주체의 개인정보 열람청구가 신속하게 처리되도록 노력하겠습니다.
► 개인정보 열람청구 접수·처리 부서
부서명: 마케팅팀
담당자: 김유림
연락처: 전화) 042-719-8104, 팩스) 042-719-8071, 이메일) yr.kim@rainbow-robotics.com
정보주체는 개인정보침해로 인한 구제를 받기 위하여 개인정보분쟁조정위원회, 한국인터넷진흥원 개인정보침해신고센터 등에 분쟁해결이나 상담 등을 신청할 수 있습니다. 이 밖에 기타 개인정보침해의 신고, 상담에 대하여는 아래의 기관에 문의하시기 바랍니다.
- 1.개인정보분쟁조정위원회 : (국번없이) 1833-6972 (www.kopico.go.kr)
- 2.개인정보침해신고센터 : (국번없이) 118 (privacy.kisa.or.kr)
- 3.대검찰청 : (국번없이) 1301 (www.spo.go.kr)
- 4.경찰청 : (국번없이) 182 (ecrm.cyber.go.kr)
「개인정보보호법」제35조(개인정보의 열람), 제36조(개인정보의 정정·삭제), 제37조(개인정보의 처리정지 등)의 규정에 의한 요구에 대 하여 공공기관의 장이 행한 처분 또는 부작위로 인하여 권리 또는 이익의 침해를 받은 자는 행정심판법이 정하는 바에 따라 행정심판을 청구할 수 있습니다.
※ 행정심판에 대해 자세한 사항은 중앙행정심판위원회(www.simpan.go.kr) 홈페이지를 참고하시기 바랍니다.
제13조(개인정보 처리방침 변경)- ①이 개인정보처리방침은 2023년 02월 10일부터 적용됩니다.
사이트 이용약관
레인보우로보틱스(이하 “회사”라 함)가 운영하는 “사용자 공간” 서비스 이용에 있어서 게시, 제공, 검색, 손해배상 및 면책에 대해서는 아래의 규정이 적용됩니다.
제1조(목적)이 약관은 레인보우로보틱스가 운영하는 사용자 공간에서 제공하는 인터넷 관련 서비스(이하 “서비스”라 함)를 이용함에 있어 사용자 공간과 이용자의 권리·의무 및 책임사항을 규정하는데 그 목적이 있습니다.
제2조(정의)- 1.“사용자 공간”이란 고객 및 협력사(Partner)가 레인보우로보틱스 협동로봇 관련 다양한 기술적 정보에 접근하고, 회원간 정보 공유가 가능한 웹사이트 플랫폼을 말합니다.
- 2.“이용자”란 “사용자 공간”에 접속하여 이 약관에 따라 회사가 제공하는 서비스를 받는 회원을 말합니다.
- 3.‘회원’이라 함은 회사에 개인정보를 제공하여 회원등록을 한 자로서, 회사의 정보를 지속적으로 제공받으며 회사가 제공하는 서비스를 이용할 수 있는 자를 말합니다.
- 1.회사는 이 약관의 내용과 상호 및 대표자 성명, 영업소 소재지 주소, 전화번호, 전자우편주소, 개인정보관리책임자 등을 이용자가 쉽게 알 수 있도록 사용자 공간 초기 서비스화면(전면)에 게시합니다. 다만, 약관의 내용은 이용자가 연결화면을 통하여 볼 수 있도록 할 수 있습니다.
- 2.회사는 이용자가 약관에 동의하기에 앞서 약관에 정해져 있는 내용 중 중요한 내용을 이용자가 이해할 수 있도록 별도의 연결화면을 제공하여 이용자의 확인을 구하여야 합니다.
- 3.회사는 「약관의 규제에 관한 법률」, 「전자문서 및 전자거래기본법」, 「전자서명법」, 「정보통신망 이용촉진 및 정보보호 등에 관한 법률」, 「소비자기본법」 등 관련 법을 위배하지 않는 범위에서 이 약관을 개정할 수 있습니다.
- 4.회사가 약관을 개정할 경우에는 적용일자 및 개정사유를 명시하여 현행약관과 함께 사용자 공간(약칭)의 초기화면에 그 적용일자 7일 이전부터 적용일자 전일까지 공지합니다. 다만, 이용자에게 불리하게 약관내용을 변경하는 경우에는 최소한 30일 이상의 사전 유예기간을 두고 공지합니다. 이 경우 회사는 개정 전 내용과 개정 후 내용을 명확하게 비교하여 이용자가 알기 쉽도록 표시합니다.
- 5.회사가 약관을 개정할 경우에는 그 개정약관은 그 적용일자 이후에 체결되는 계약에만 적용되고 그 이전에 이미 체결된 계약에 대해서는 개정 전의 약관조항이 그대로 적용됩니다. 다만 이미 계약을 체결한 이용자가 개정약관 조항의 적용을 받기를 원하는 뜻을 제3항에 의한 개정약관의 공지기간 내에 회사에 송신하여 회사의 동의를 받은 경우에는 개정약관 조항이 적용됩니다.
-
1.“사용자 공간”은 다음과 같은 업무를 수행합니다.
- ①협동로봇에 대한 기술정보 제공
- ②회원간 정보 공유가 가능한 포럼 사이트 운영
- ③기타 사용자 공간이 정하는 업무
- 2.“사용자 공간”은 제품의 품절 또는 기술적 사양의 변경 등의 경우에는 장차 체결되는 계약에 의해 제공할 재화 또는 용역의 내용을 변경할 수 있습니다. 이 경우에는 변경된 재화 또는 용역의 내용 및 제공일자를 명시하여 현재의 재화 또는 용역의 내용을 게시한 곳에 즉시 공지합니다.
- 3.“사용자 공간”이 제공하기로 이용자와 계약을 체결한 서비스의 내용을 재화 등의 품절 또는 기술적 사양의 변경 등의 사유로 변경할 경우에는 그 사유를 이용자에게 통지 가능한 주소로 즉시 통지합니다.
- 4.전항의 경우 “회사”는 이로 인하여 이용자가 입은 손해를 배상합니다. 다만, “사용자 공간”이 고의 또는 과실이 없음을 입증하는 경우에는 그러하지 아니합니다.
- 1.“사용자 공간”은 컴퓨터 등 정보통신설비의 보수점검․교체 및 고장, 통신의 두절 등의 사유가 발생한 경우에는 서비스의 제공을 일시적으로 중단할 수 있습니다.
- 1.이용자는 “사용자 공간”이 정한 가입 양식에 따라 회원정보를 기입한 후 이 약관에 동의한다는 의사표시를 함으로서 회원가입을 신청합니다.
-
2.“사용자 공간”은 제1항과 같이 회원으로 가입할 것을 신청한 이용자 중 다음 각 호에 해당하지 않는 한 회원으로 등록합니다.
- ①가입신청자가 이 약관 제7조제3항에 의하여 이전에 회원자격을 상실한 적이 있는 경우, 다만 제7조제3항에 의한 회원자격 상실 후 3년이 경과한 자로서 “사용자 공간”의 회원재가입 승낙을 얻은 경우에는 예외로 한다.
- ②등록 내용에 허위, 기재누락, 오기가 있는 경우
- ③기타 회원으로 등록하는 것이 “사용자 공간”의 기술상 현저히 지장이 있다고 판단되는 경우
- 3.회원가입계약의 성립 시기는 “사용자 공간”의 승낙이 회원에게 도달한 시점으로 합니다.
- 4.회원은 회원가입 시 등록한 사항에 변경이 있는 경우, 상당한 기간 이내에 “사용자 공간”에 대하여 회원정보 수정 등의 방법으로 그 변경사항을 알려야 합니다.
- 1.회원은 “회사”에 언제든지 탈퇴를 요청할 수 있으며 “회사”는 즉시 회원탈퇴를 처리합니다.
-
2.회원이 다음 각 호의 사유에 해당하는 경우, “회사”는 회원자격을 제한 및 정지시킬 수 있습니다.
- ①가입 신청 시에 허위 내용을 등록한 경우
- ②다른 사람의 “사용자 공간” 이용을 방해하거나 그 정보를 도용하는 등 질서를 위협하는 경우
- ③“사용자 공간”을 이용하여 법령 또는 이 약관이 금지하거나 공서양속에 반하는 행위를 하는 경우
- ④“회사”가 회원 자격을 제한․정지시킨 후, 동일한 행위가 2회 이상 반복되거나 30일 이내에 그 사유가 시정되지 아니하는 경우 “회사”는 회원자격을 상실 시킬 수 있습니다.
- ⑤“회사”가 회원자격을 상실시키는 경우에는 회원등록을 말소합니다. 이 경우 회원에게 이를 통지하고, 회원등록 말소 전에 최소한 30일 이상의 기간을 정하여 소명할 기회를 부여합니다.
- 1.“회사”가 회원에 대한 통지를 하는 경우, 회원이 “회사”와 미리 약정하여 지정한 전자우편 주소로 할 수 있습니다.
- 2.“회사”는 불특정다수 회원에 대한 통지의 경우 1주일 이상 “사용자 공간” 게시판에 게시함으로써 개별 통지에 갈음할 수 있습니다. 다만, 회원 본인과 관련하여 중대한 영향을 미치는 사항에 대하여는 개별통지를 합니다.
- 1.“회사”가 제3자에게 이용자의 개인정보를 제공할 필요가 있는 경우 1) 개인정보를 제공받는 자, 2)개인정보를 제공받는 자의 개인정보 이용목적, 3) 제공하는 개인정보의 항목, 4) 개인정보를 제공받는 자의 개인정보 보유 및 이용기간을 구매자에게 알리고 동의를 받아야 합니다. (동의를 받은 사항이 변경되는 경우에도 같습니다.)
- 2.“사용자 공간”이 제3자에게 구매자의 개인정보를 취급할 수 있도록 업무를 위탁하는 경우에는 1) 개인정보 취급위탁을 받는 자, 2) 개인정보 취급위탁을 하는 업무의 내용을 구매자에게 알리고 동의를 받아야 합니다. (동의를 받은 사항이 변경되는 경우에도 같습니다.) 다만, 서비스제공에 관한 계약이행을 위해 필요하고 구매자의 편의증진과 관련된 경우에는 「정보통신망 이용촉진 및 정보보호 등에 관한 법률」에서 정하고 있는 방법으로 개인정보 취급방침을 통해 알림으로써 고지절차와 동의절차를 거치지 않아도 됩니다.
- 1.“회사”는 이용자의 개인정보 수집 시 서비스제공을 위하여 필요한 범위에서 최소한의 개인정보를 수집합니다.
- 2.“회사”는 회원가입 시 구매계약이행에 필요한 정보를 미리 수집하지 않습니다. 다만, 관련 법령상 의무이행을 위하여 구매계약 이전에 본인확인이 필요한 경우로서 최소한의 특정 개인정보를 수집하는 경우에는 그러하지 아니합니다.
- 3.“회사”는 이용자의 개인정보를 수집·이용하는 때에는 당해 이용자에게 그 목적을 고지하고 동의를 받습니다.
- 4.“회사”는 수집된 개인정보를 목적 외의 용도로 이용할 수 없으며, 새로운 이용목적이 발생한 경우 또는 제3자에게 제공하는 경우에는 이용·제공단계에서 당해 이용자에게 그 목적을 고지하고 동의를 받습니다. 다만, 관련 법령에 달리 정함이 있는 경우에는 예외로 합니다.
- 5.“회사”가 제2항과 제3항에 의해 이용자의 동의를 받아야 하는 경우에는 개인정보관리 책임자의 신원(소속, 성명 및 전화번호, 기타 연락처), 정보의 수집목적 및 이용목적, 제3자에 대한 정보제공 관련사항(제공받은 자, 제공목적 및 제공할 정보의 내용) 등 「정보통신망 이용촉진 및 정보보호 등에 관한 법률」 제22조제2항이 규정한 사항을 미리 명시하거나 고지해야 하며 이용자는 언제든지 이 동의를 철회할 수 있습니다.
- 6.“회사”는 개인정보 보호를 위하여 이용자의 개인정보를 취급하는 자를 최소한으로 제한하여야 하며 이용자의 개인정보의 분실, 도난, 유출, 동의 없는 제3자 제공, 변조 등으로 인한 이용자의 손해에 대하여 모든 책임을 집니다.
- 7.“회사” 또는 그로부터 개인정보를 제공받은 제3자는 개인정보의 수집목적 또는 제공받은 목적을 달성한 때에는 당해 개인정보를 지체 없이 파기합니다.
- 8.“회사”는 개인정보의 수집·이용·제공에 관한 동의 란을 미리 선택한 것으로 설정해두지 않습니다. 또한 개인정보의 수집·이용·제공에 관한 이용자의 동의거절 시 제한되는 서비스를 구체적으로 명시하고, 필수수집항목이 아닌 개인정보의 수집·이용·제공에 관한 이용자의 동의 거절을 이유로 회원가입 등 서비스 제공을 제한하거나 거절하지 않습니다.
- 1.“사용자 공간”은 법령과 이 약관이 금지하거나 공서양속에 반하는 행위를 하지 않으며 이 약관이 정하는 바에 따라 지속적이고, 안정적으로 재화․용역을 제공하는데 최선을 다하여야 합니다.
- 2.“사용자 공간”은 이용자가 안전하게 인터넷 서비스를 이용할 수 있도록 이용자의 개인정보(신용정보 포함)보호를 위한 보안 시스템을 갖추어야 합니다.
- 3.“사용자 공간”이 상품이나 용역에 대하여 「표시․광고의 공정화에 관한 법률」 제3조 소정의 부당한 표시․광고행위를 함으로써 이용자가 손해를 입은 때에는 이를 배상할 책임을 집니다.
- 4.“사용자 공간”은 이용자가 원하지 않는 영리목적의 광고성 전자우편을 발송하지 않습니다.
- 1.제17조의 경우를 제외한 ID와 비밀번호에 관한 관리책임은 회원에게 있습니다.
- 2.회원은 자신의 ID 및 비밀번호를 제3자에게 이용하게 해서는 안됩니다.
- 3.회원이 자신의 ID 및 비밀번호를 도난당하거나 제3자가 사용하고 있음을 인지한 경우에는 바로 “회사”에 통보하고 “회사”의 안내가 있는 경우에는 그에 따라야 합니다.
- 1.신청 또는 변경 시 허위 내용의 등록
- 2.타인의 정보 도용
- 3.“회사”가 정한 정보 이외의 정보(컴퓨터 프로그램 등) 등의 송신 또는 게시
- 4.기타 제3자의 저작권 등 지적재산권에 대한 침해
- 5.기타 제3자의 명예를 손상시키거나 업무를 방해하는 행위
- 6.외설 또는 폭력적인 메시지, 화상, 음성, 기타 공서양속에 반하는 정보를 사용자 공간에 공개 또는 게시하는 행위
- 1.회사가 작성한 “사용자 공간” 저작물에 대한 저작권 기타 지적재산권은 ”회사“에 귀속합니다.
- 2.이용자는 “사용자 공간”을 이용함으로써 얻은 정보 중 “회사”에게 지적재산권이 귀속된 정보를 “회사”의 사전 승낙 없이 복제, 송신, 출판, 배포, 방송 기타 방법에 의하여 영리목적으로 이용하거나 제3자에게 이용하게 하여서는 안됩니다.
- 3.“회사”는 약정에 따라 이용자에게 귀속된 저작권을 사용하는 경우 당해 이용자에게 통보하여야 합니다.